What is a Roll Lamination Machine and How Does It Work?
In the world of manufacturing, the Roll Lamination Machine plays a crucial role. This equipment is designed to bond layers of materials together, creating durable and high-quality products. According to industry expert Mark Thompson, "The efficiency of a Roll Lamination Machine can significantly impact production speed and cost-effectiveness." His insight underscores the machine's importance in modern industrial processes.
The operations of a Roll Lamination Machine are fascinating yet complex. It utilizes heat and pressure to merge materials seamlessly. As materials pass through rollers, they undergo transformations that enhance their properties. This process can be meticulously controlled to achieve desired results. However, it requires expertise and careful calibration. Imperfect settings can lead to subpar products, revealing the necessity of skilled operators.
Understanding the Roll Lamination Machine's function reveals its influence on various industries. Packaging, automotive, and textiles rely on this technology. Its adaptability makes it suitable for different materials and applications. Nevertheless, challenges arise, such as material compatibility and maintenance issues. Continuous improvement and innovation in this field are essential to maximize efficiency and quality in production.
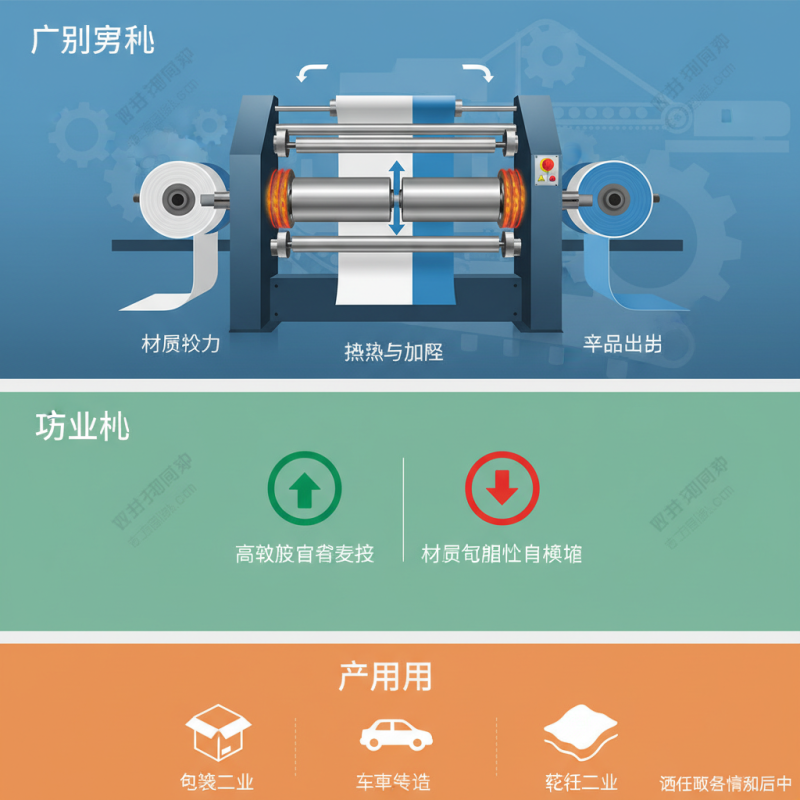
What is a Roll Lamination Machine? An Overview of its Purpose and Function
A roll lamination machine is a vital tool in many industries. This device bonds materials together using heat and pressure. The process creates a durable finish that protects items from damage. It is widely used for films, papers, and other substrates. Many products benefit from this laminating technique, improving visual appeal and longevity.
The machine typically consists of rollers that apply adhesive between layers. As materials pass through, they are subjected to heat and pressure. This ensures a strong bond. Understanding its function is important for maximizing efficiency. However, not all machines are the same. Some may require adjustments to achieve optimal results.
Operators must monitor settings closely. Small changes can impact the final product. Overheating can damage materials, while low pressure may result in weak bonds. Experimenting with different settings can yield better outcomes. Like any technology, roll lamination machines demand careful handling. The process is not foolproof, and mistakes can lead to disappointing results.
Key Components of a Roll Lamination Machine: Understanding the Mechanism
A roll lamination machine is designed to apply protective and decorative films to various materials. Understanding its key components helps in grasping how it operates. At the core of the machine are the rollers. These rollers apply pressure and heat uniformly. They facilitate the adhesion of the lamination film to the substrate. The rollers need to maintain a precise alignment. Misalignment can lead to issues, such as uneven lamination.
Another crucial element is the feeding mechanism. It ensures a smooth and controlled input of the material. If the feeding is inconsistent, it may cause bubbles or wrinkles. The temperature controls are also vital. Incorrect temperatures can make the film warp or fail to stick. Operators often face challenges in maintaining these settings. Calibration errors can yield unsatisfactory results.
Moreover, the control panel plays a significant role. It allows operators to monitor and adjust parameters. User interface design can be complex. Some operators find it challenging to navigate. Average operators may overlook important adjustments. These details can significantly impact the lamination process. Continuous training and familiarization with the machine are necessary. Recognizing these components can lead to better operation and fewer errors.
The Roll Lamination Process: Step-by-Step Guide to Operation
The roll lamination process involves a series of precise steps essential for producing high-quality laminated materials. This technique utilizes heat and pressure to bond layers together. The process starts with the preparation of substrates. These substrates can be paper, plastic, or metal films, depending on the desired end product. Common thicknesses range from 1mil to 10mils, impacting durability and flexibility.
After substrate preparation, the roll lamination machine feeds the materials through heated rollers. The temperature and pressure applied are critical. Industry studies indicate that the ideal temperature for materials can range from 250°F to 350°F. This heat causes the adhesive to activate, binding layers tightly. It's essential to monitor this closely; too much heat can warp the substrates.
Post-lamination, cooling takes place to set the bond. This is where imperfections can arise. Sometimes, uneven cooling leads to delamination issues. According to recent reports, about 15% of laminated products show some form of defect. Therefore, quality checks are necessary throughout the process. Adjustments might be needed based on real-time observations. Understanding these steps thoroughly helps in achieving optimal results.
Applications of Roll Lamination Machines in Various Industries
Roll lamination machines play a crucial role across various industries. They provide a method for bonding materials together. This process enhances durability and adds aesthetic appeal to products. In packaging, roll lamination is common for creating moisture-resistant barriers. Food industries often utilize this, ensuring products stay fresh longer.
In the automotive sector, these machines are employed for laminating composite materials. This can enhance lightweight construction, contributing to fuel efficiency. Yet, it’s important to note that not all laminating methods work universally. Each material presents unique challenges. Understanding these factors is vital for effective results.
Electronics manufacturing also benefits from roll lamination. It is used for creating flexible circuits. This allows for innovation in compact device designs. However, quality control is a constant concern. Small imperfections can lead to significant failures. Adequate testing and precise adjustments are necessary for success.
What is a Roll Lamination Machine and How Does It Work? - Applications of Roll Lamination Machines in Various Industries
| Industry | Applications | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Lamination of window films and insulation materials | Enhanced thermal efficiency and UV protection |
| Electronics | Laminating flexible circuits and component materials | Improved durability and functionality |
| Packaging | Production of laminated packaging films | Increased product shelf life and barrier properties |
| Construction | Laminating building materials like panels and membranes | Enhanced strength and weather resistance |
| Textiles | Laminating fabrics for protective clothing | Improved water resistance and durability |
Market Trends and Innovations in Roll Lamination Technology
Roll lamination technology has been evolving rapidly, reflecting current market trends. This process involves bonding materials through heat and pressure. Manufacturers are now embracing automation. Smart machines are making the process more efficient. Reduced labor costs are a significant advantage. Yet, this shift raises concerns about skill gaps in the workforce.
Sustainability is becoming a key focus in roll lamination. Companies are exploring eco-friendly materials and processes. Biodegradable films are gaining traction. While this is promising, not all manufacturers are ready to adopt these innovations. Some hesitate due to cost implications. Additionally, the challenge of recycling laminated products remains unresolved. It’s a complex issue that needs more attention.
The demand for customized solutions is rising. Businesses seek unique offerings to differentiate themselves. This trend has led to more flexible lamination options. However, the need for speed can compromise quality. Balancing these elements is crucial. As the industry advances, continuous reflection on these challenges will drive future innovations.